Your Guide To Coping With Separation Anxiety In Relationships
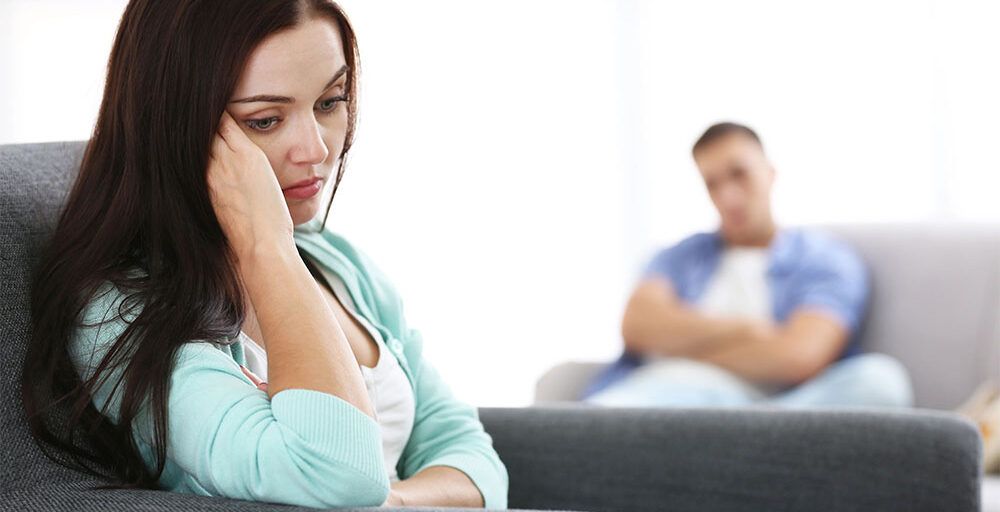
Separation anxiety in relationships can create feelings of distress when partners are apart. This emotional discomfort often leads to excessive worry, fear of abandonment, or intrusive thoughts. People experiencing separation anxiety may constantly check in with their partner, feel insecure about their relationship, or struggle with trust.
While this anxiety is common in early relationships, it can also persist and interfere with daily life. Recognizing the signs of this anxiety is the first step toward managing it and improving relationship dynamics.
Understanding Separation Anxiety in Relationships
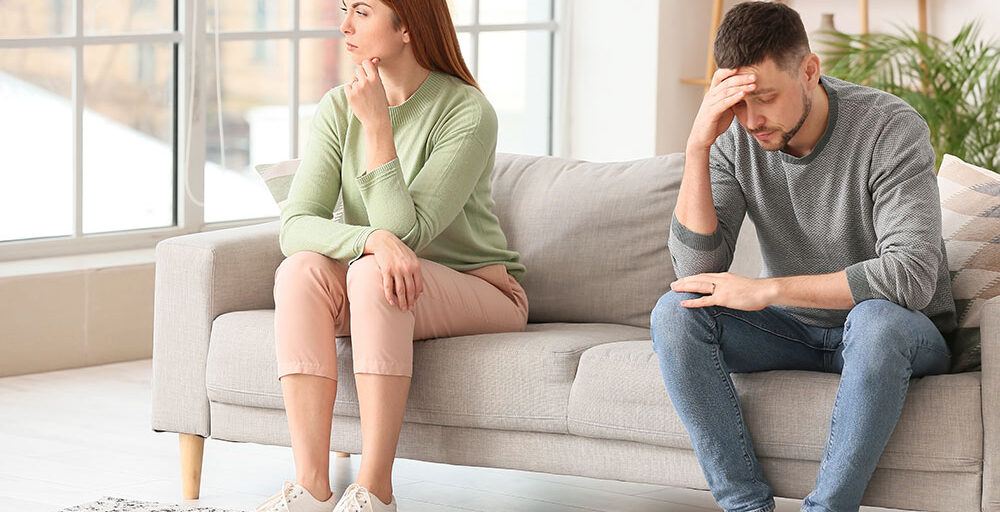
Separation anxiety is typically associated with children, but it can manifest in adults as well. In relationships, it arises when one person experiences heightened distress due to the physical or emotional absence of their partner.
This anxiety is not necessarily a sign of an unhealthy relationship, but it can strain communication and lead to emotional difficulties. The fear of being left behind or rejected can lead to behaviors such as clinginess, jealousy, or difficulty being apart from the partner for even short periods.
Why Anxiety Feels Overwhelming
When anxiety takes hold, the emotional distress can be overwhelming. It triggers a fight-or-flight response in the body, causing feelings of panic, heart racing, and physical discomfort. These responses may not be proportional to the situation at hand but are a result of the brain perceiving the absence as a potential threat to the relationship.
Individuals may find themselves caught in a cycle of worrying about what could go wrong, making it hard to stay grounded in the present moment.
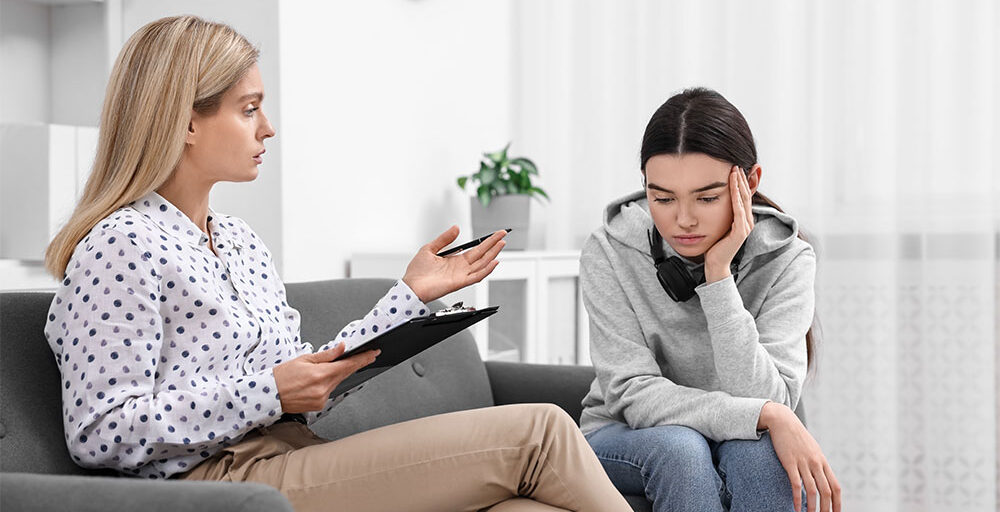
Therapy Options for Coping
Therapy can offer practical solutions for those dealing with separation anxiety in relationships. Individual therapy, such as cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), helps individuals challenge negative thought patterns that contribute to their anxiety. A therapist can guide you in reframing thoughts and managing irrational fears.
Group therapy, on the other hand, allows individuals to share their experiences with others facing similar struggles, providing support and reassurance. Together, these therapies can help you understand the roots of your anxiety and develop healthier coping mechanisms.
Advanced Treatments for Anxiety
For some, traditional therapy might not fully address the anxiety. This is where treatments like transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) may be beneficial. TMS is a non-invasive technique that utilizes magnetic fields to target brain regions involved in mood regulation.
It provides a promising option for treating depression and anxiety, especially for individuals who have not found success with other approaches. While it is not a cure-all, many people find relief through this innovative approach.
Building Stronger Relationships with Healthy Boundaries
Managing separation anxiety involves more than just treating the symptoms—it requires a shift in how one views the relationship and the self. It is important to develop healthy boundaries and maintain a sense of individuality within the partnership.
Engaging in activities that nurture self-esteem and confidence outside of the relationship can also help reduce anxiety. By focusing on self-care and trust-building, you can start to experience more balance and peace in your connection.
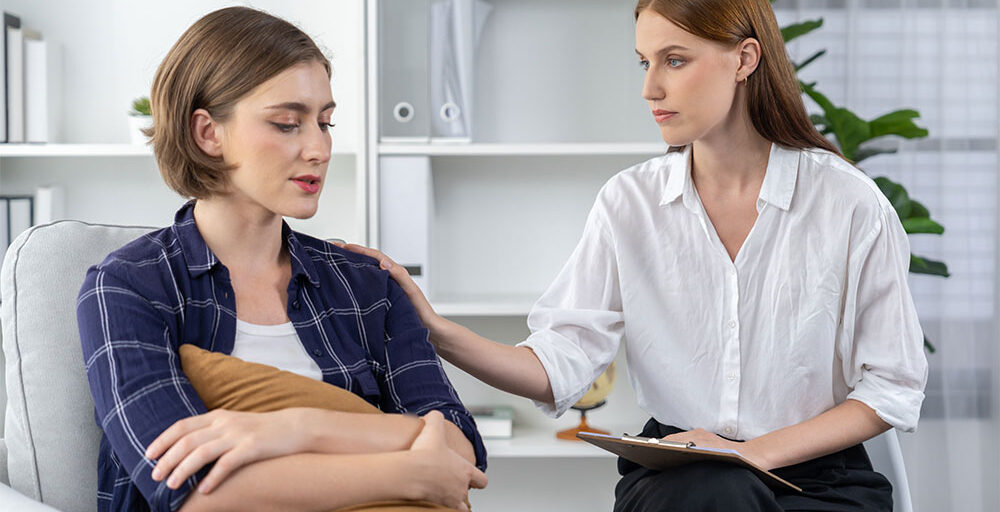
Supporting Your Mental Health at Wonder Years Psychiatric Services
At Wonder Years Psychiatric Services, we understand the emotional struggles that come with separation anxiety in relationships. Our approach is rooted in compassion, and we aim to help you navigate these challenges through a blend of therapy and innovative treatments like TMS.
Our team works closely with you to develop tailored strategies that promote emotional well-being and strengthen your relationships. You do not have to face these struggles alone; we are here to support you every step of the way.