The Role Of Psychologist For Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is a complex neurodevelopmental condition that requires specialized, multi-faceted care. A psychologist for autism plays an important role in providing individualized support, from diagnosis to therapeutic interventions, for those with ASD. With expertise in behavior, cognition, and emotional support, psychologists are important in enhancing the quality of life for individuals with autism.
Why a Psychologist is Vital for Autism
A psychologist for autism assists not only with diagnosis but also with creating structured therapy plans that support the unique needs of each individual. From understanding behavior patterns to helping families manage daily challenges, psychologists bring valuable insight to autism care. Their work often complements that of other specialists and provides a holistic approach to ASD treatment and support.
Diagnostic Assessment and Early Intervention
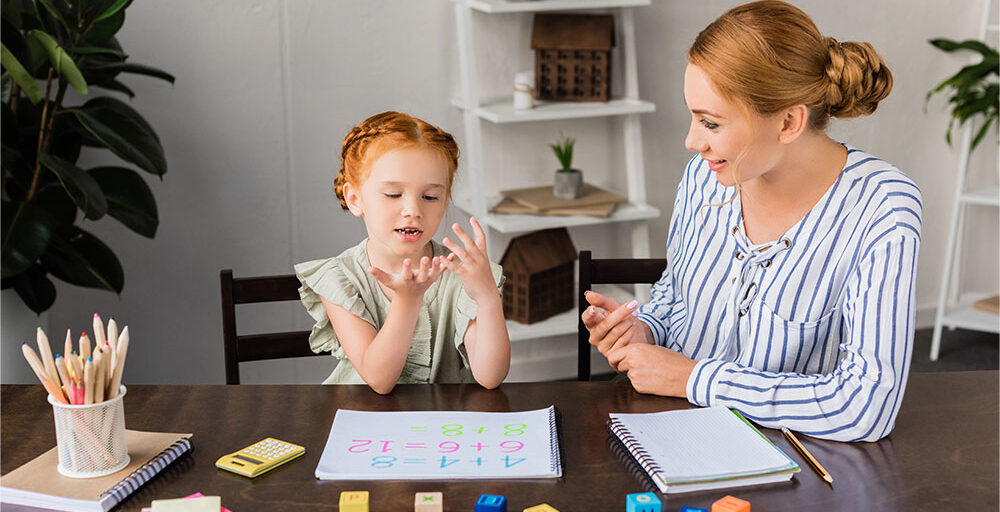
Early diagnosis and intervention are key to improving outcomes for individuals with ASD, and psychologists are usually integral in these initial stages. Using tools like structured interviews, cognitive assessments, and behavioral observations, psychologists identify developmental markers of ASD. Early intervention through psychological assessments helps establish a clear treatment path, as cited by Verywell Health.
Psychologists use validated screening tools, often incorporating feedback from parents and caregivers. This comprehensive evaluation informs individualized therapy plans and allows families to understand their loved one’s strengths and areas for development.
Therapeutic Approaches for Autism
Psychologists utilize several therapeutic models that benefit individuals with ASD. Applied Behavior Analysis (ABA), which focuses on reinforcing positive behaviors, is one of the most commonly used interventions in autism care. Additionally, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is employed to address co-occurring conditions like anxiety or depression. This approach can be particularly impactful for teenagers and adults with autism.
For younger children, developmental models like the SCERTS approach or Floortime emphasize social communication and emotional growth. These therapies can be tailored to the child’s developmental level, thereby, promoting more effective engagement and adaptability.
Family and Group Therapy in Autism Care
Family involvement is often a significant part of autism treatment, and psychologists offer individual and group therapy to strengthen family dynamics. Family therapy provides parents and siblings with strategies to interact more effectively with their loved one who has autism. Psychologists guide families in understanding behaviors and fostering positive relationships to create a supportive home environment.
Additionally, group therapy with peers can offer individuals with autism valuable opportunities for social interaction. These sessions encourage social skills development and help individuals with ASD feel connected to others facing similar experiences.
Monitoring Progress and Adjusting Treatment Plans
A psychologist’s role does not end after initial assessments and interventions; they continue to monitor progress and adjust therapy plans as needed. Regular evaluations help psychologists track behavioral changes, adapt therapies to the individual’s evolving needs, and provide ongoing guidance for families. A sustained involvement can contribute to a more consistent and effective treatment experience.
Psychologists may also coordinate with other healthcare providers, such as psychiatrists, if medication or additional interventions become necessary. This collaborative approach enhances the quality and continuity of care, which benefits both individuals with autism and their families.
Supporting Individuals with ASD Every Step of the Way
Wonder Years Psychiatric Services is dedicated to helping individuals with autism spectrum disorder achieve their fullest potential. Through comprehensive therapy and family support, we work closely with you to create positive outcomes. Reach out to learn how we can assist you in treating autism spectrum disorder and enhancing your well-being.