Anxiety Therapy Vs. Medication: Which Works Best?
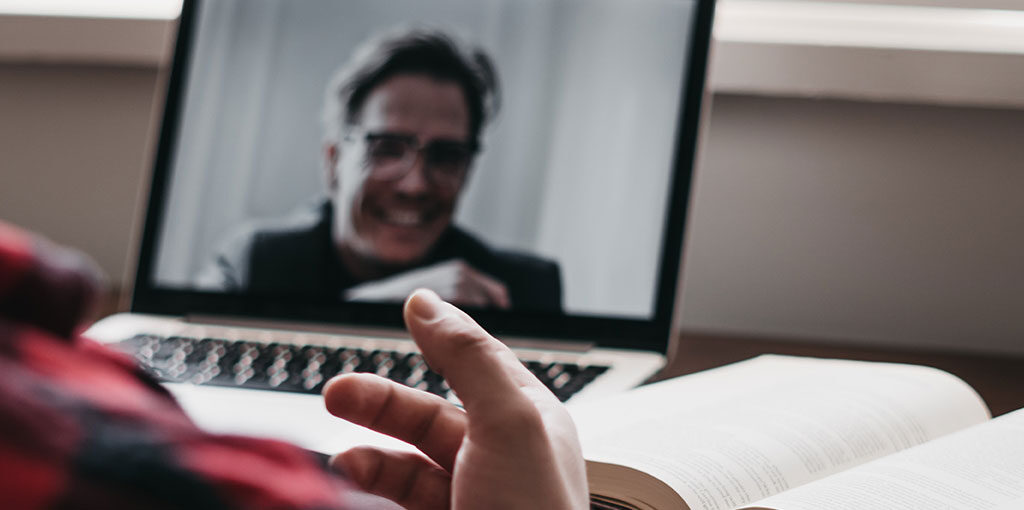
Anxiety therapy, also known as psychotherapy or counseling, provides individuals with a safe space to explore the root causes of their anxiety. Through therapeutic sessions, individuals can develop practical coping skills, gaining the tools to regain control over their thoughts and emotions. Conversely, medication can offer rapid relief from acute symptoms, providing a stabilizing effect on mood and reducing the intensity of anxiety.
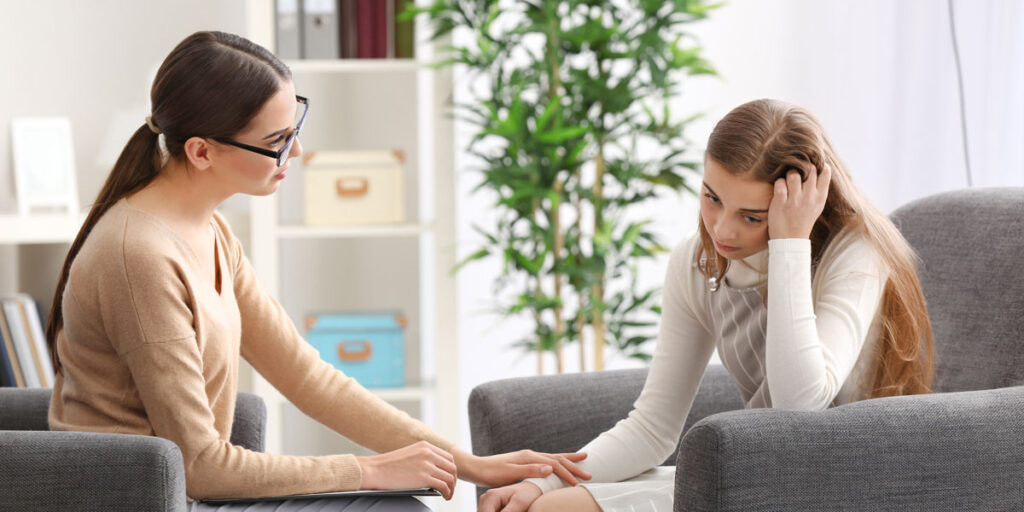
Personalized Anxiety Therapy: A Journey to Well-being
Anxiety therapy, often referred to as psychotherapy or counseling, provides individuals with a safe space to explore the root causes of their anxiety. This approach involves talking to a trained therapist who employs various techniques to help clients understand and manage their anxiety triggers. Here are some key benefits:
Therapy equips individuals with practical skills to cope with anxiety-inducing situations, such as relaxation techniques, mindfulness, and cognitive-behavioral strategies. These skills empower individuals to regain control over their thoughts and emotions, fostering a sense of self-reliance and resilience.
Moreover, therapy focuses on addressing the underlying causes of anxiety, offering the potential for lasting relief without relying on medication. By delving into the emotional and psychological factors contributing to stress, therapy provides individuals with the tools to confront and overcome their fears and worries.
Wonder Years Psychology focuses on providing personalized anxiety therapy tailored to each individual’s unique needs. This approach encompasses a variety of techniques, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, mindfulness, and stress management strategies. Recognizing that anxiety manifests differently in everyone, Wonder Years’ expert therapists work closely with clients to develop a deep understanding of their specific challenges. By creating a supportive and understanding environment, they empower individuals to uncover the root causes of their anxiety, develop coping strategies, and build resilience. This personalized approach ensures that therapy is about managing symptoms and fostering long-term mental health and well-being.
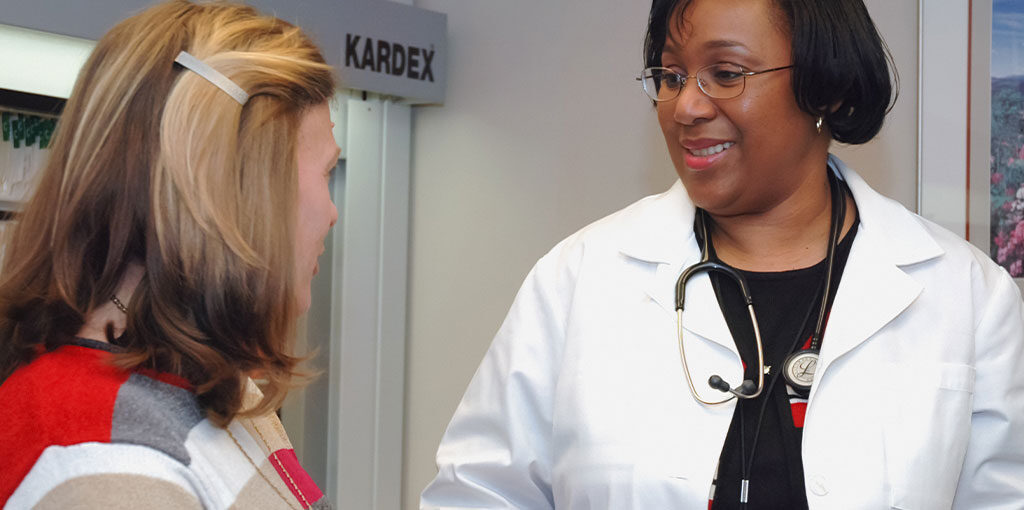
Medication Management: A Critical Component of Anxiety Treatment
Medication, on the other hand, can be an effective tool for managing anxiety symptoms, especially in cases of severe or debilitating anxiety. Here are some advantages:
One significant benefit of medication is its ability to provide rapid relief from acute anxiety symptoms. When anxiety becomes overwhelming, medication can swiftly alleviate the distressing symptoms, helping individuals regain their emotional balance. This quick relief can be essential for those facing a crisis or severe anxiety episodes.
Furthermore, medication can stabilize mood and reduce the intensity of anxiety. This stabilization can make it easier for individuals to engage in therapy and learn coping skills. By reducing the overwhelming sense of anxiety, medication can create a more conducive environment for individuals to work on the psychological aspects of their anxiety in therapy sessions.
While medication offers these benefits, it’s important to remember that it is not a standalone solution for anxiety. It typically works best in conjunction with therapy to address the underlying causes of anxiety and develop coping strategies for the long term.
In addition to therapy, Wonder Years Psychology also offers expert guidance in medication management as part of a comprehensive anxiety treatment plan. Medication can be an essential tool for some individuals, helping to reduce symptoms and provide relief. The experienced psychiatrists at Wonder Years evaluate each client’s needs carefully, considering factors like symptoms’ severity and co-occurring conditions. They aim to provide a balanced and practical treatment approach by combining medication with therapy. Medication management at Wonder Years is not just about prescribing pills; it’s about monitoring progress, adjusting dosages, and ensuring that each client receives the most beneficial treatment for their specific situation.
Start Your Journey to Recovery Today
Are you or a loved one struggling with anxiety? Take the first step toward healing with Wonder Years Psychology. Our team of compassionate professionals is ready to support you through personalized therapy and comprehensive treatment plans. Whether you’re considering therapy, medication, or a combination of both, we’re here to guide you on your journey to recovery. Contact Wonder Years Psychology today and begin your journey to a healthier, more peaceful life. Your mental health is our priority.