Does Too Much Screen Time Cause ADHD In Children?
The rise of digital devices has sparked debates among parents, educators, and healthcare professionals about their impact on children’s health. One pressing question is, “does too much screen time cause ADHD?” Let us take current research into account while uncovering the connection between excessive screen time and the development of ADHD in children.
Understanding ADHD
Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), is a neurodevelopmental disorder with patterns of impulsivity, hyperactivity, and inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. Children with ADHD often struggle with school performance, social interactions, and maintaining focus on tasks. As pointed out by Cleveland Clinic, the disorder affects approximately 5-10% of children worldwide, making it a significant public health concern.
The Role of Screen Time
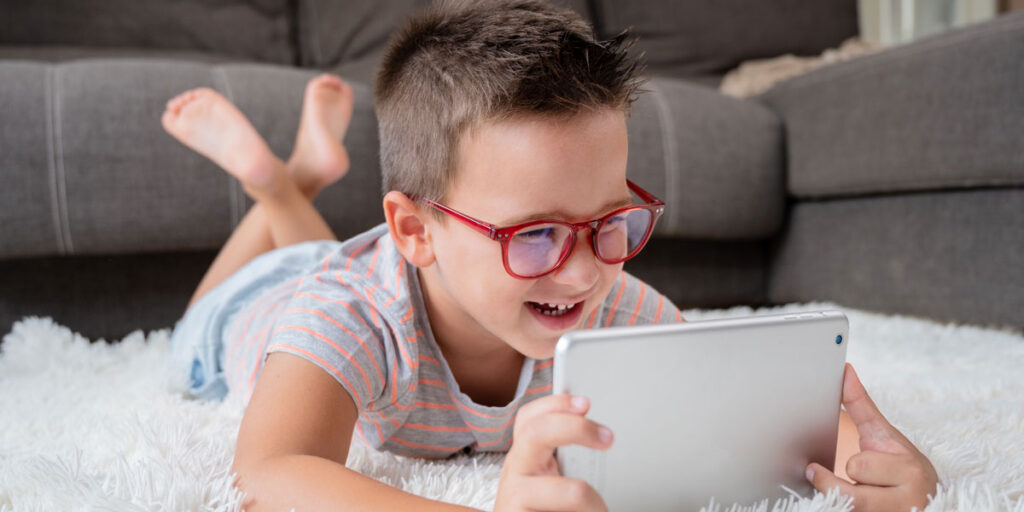
Screen time encompasses the use of digital devices such as smartphones, tablets, computers, and televisions. With the increasing prevalence of these devices, children are spending more time in front of screens than ever before. This shift has led researchers to explore whether there is a link between screen time and the development or exacerbation of ADHD symptoms.
Research Findings
Several studies have investigated the relationship between screen time and ADHD. According to a study cited by the Cleveland Clinic, excessive screen time can be associated with an increase in ADHD-related behaviors. The research found that children who spent more than two hours per day on screens were more likely to exhibit symptoms such as inattention and hyperactivity.
Another study published in the Journal of the American Medical Association (JAMA) Pediatrics examined over 2,500 children and found a significant correlation between high screen time and the development of ADHD symptoms. The researchers concluded that children who engage in prolonged screen use are at a higher risk of developing attention-related problems.
Mechanisms behind the Link
The exact mechanisms by which screen time might influence ADHD are still being explored. One theory is that the fast-paced and highly stimulating nature of digital content may alter brain development, making it harder for children to maintain attention in less stimulating environments. Additionally, excessive screen time can interfere with sleep, physical activity, and face-to-face social interactions, all of which are crucial for healthy cognitive and emotional development.
Balancing Screen Time and Healthy Development
While screens are an integral part of modern life, it is essential to balance their use to promote healthy development. The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends that children should be given limits with media use, pointing out that those between two and five years should not exceed their screen time to over one hour per day. Encouraging activities such as outdoor play, reading, and family interactions can help mitigate the potential negative effects of screen time.
Wonder Years Psychiatric Services PLLC: Offering Professional Support
If you are concerned about your child’s screen time and its potential impact on their attention and behavior, professional support can make a significant difference. Wonder Years Psychiatric Services PLLC provides comprehensive ADHD coaching services designed to help children and their families manage ADHD symptoms effectively. Our team of experts provides personalized strategies to improve focus, organization, and overall well-being. Contact us today to learn more about how we can support your child’s journey toward a balanced and fulfilling life.