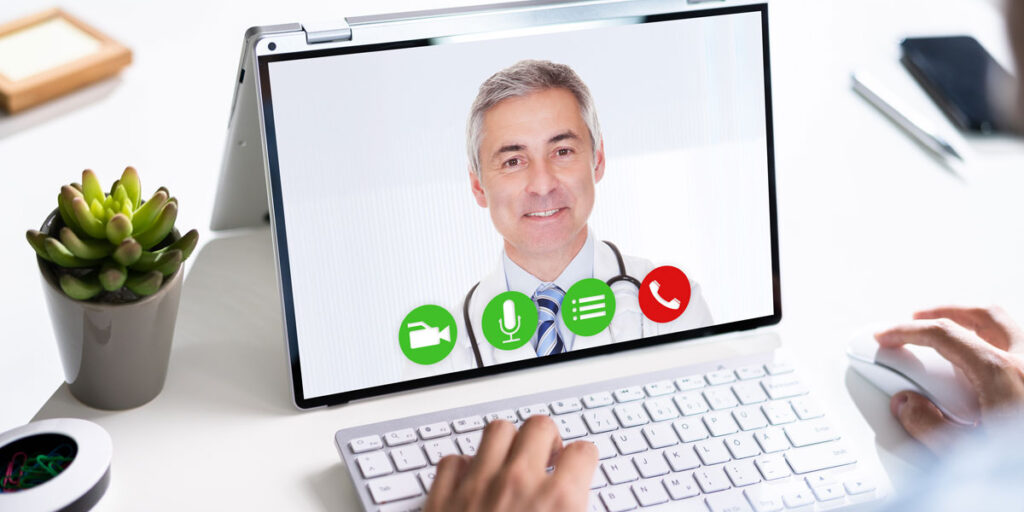
What To Expect From Your First Telepsychiatry Appointment
Accessing mental health care has become more convenient and flexible, thanks to telepsychiatry. If you’re considering scheduling a telepsychiatry appointment for the first time, you might have questions about what to expect. This blog post will guide you through the process, from preparation to the actual session, and highlight the benefits of virtual psychiatric consultations.
Preparing for Your Telepsychiatry Appointment
- Choosing the Right Environment: Selecting a quiet, private space for your telepsychiatry appointment is essential. This ensures that you can speak openly with your psychiatrist without distractions or interruptions. Make sure the area is well-lit and comfortable, as this will help you feel more at ease during the session.
- Technical Requirements: Before your appointment, check that you have a reliable internet connection, a computer or mobile device with a camera, and a headset or headphones if necessary. Test your equipment beforehand to avoid technical issues during your session. Familiarize yourself with the telepsychiatry platform you’ll be using, and ensure you know how to log in and navigate the interface.
- Gathering Necessary Information: Having all the relevant information at hand can help your telepsychiatry appointment run smoothly. Prepare a list of your current medications, any previous psychiatric diagnoses, and any questions or concerns you want to discuss. Additionally, having a notepad ready can be useful for jotting down important points during the session.
The Telepsychiatry Session
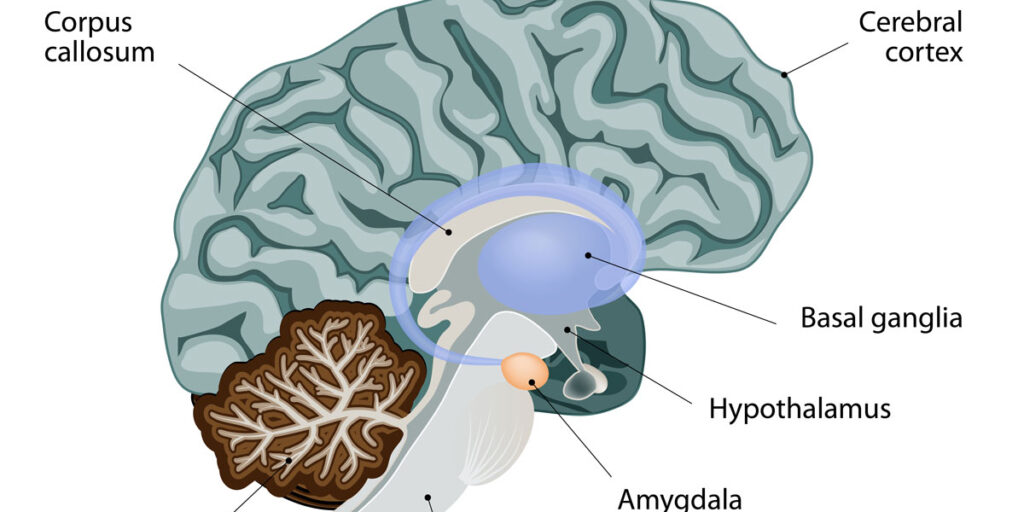
- Initial Assessment: During your first telepsychiatry appointment, your psychiatrist will conduct a comprehensive assessment to understand your mental health needs. This will involve discussing your medical history, current symptoms, and any previous treatments you have tried. The psychiatrist may also ask about your lifestyle, relationships, and any stressors you are currently facing.
- Building Rapport: Building a therapeutic relationship is a key component of effective mental health care. Your psychiatrist will take the time to establish rapport and create a comfortable, supportive environment. This initial interaction sets the foundation for ongoing treatment and collaboration.
- Treatment Plan Development: Based on the assessment, your psychiatrist will work with you to develop a personalized treatment plan. This may include recommendations for medication, therapy, or other interventions tailored to your specific needs. Your psychiatrist will explain the rationale behind each recommendation and address any concerns you may have.
Benefits of Telepsychiatry
- Convenience and Accessibility: Telepsychiatry offers unparalleled convenience, allowing you to access mental health care from the comfort of your own home. This is especially beneficial for individuals living in remote areas or those with mobility issues. With telepsychiatry, you can schedule appointments that fit seamlessly into your routine, reducing the need for travel and time off work.
- Continuity of Care: Telepsychiatry ensures continuity of care, even when circumstances prevent in-person visits. Whether you are traveling, relocating, or facing health concerns that limit your ability to visit a clinic, telepsychiatry enables you to maintain regular contact with your psychiatrist and adhere to your treatment plan.
- Enhanced Comfort: Many patients find the familiar surroundings of their own homes more comfortable than a clinical setting. This increased comfort can facilitate open communication and help patients feel more relaxed during their appointments. Telepsychiatry can also reduce the anxiety some individuals experience when visiting a healthcare facility.
Addressing Common Concerns
- Privacy and Confidentiality: Privacy is a top priority in telepsychiatry. Reputable telepsychiatry platforms use secure, encrypted connections to protect your personal information. Your psychiatrist will also take measures to ensure that your session is conducted in a private setting, free from interruptions.
- Effectiveness: Research has shown that telepsychiatry is as effective as in-person psychiatric care for many mental health conditions. The key to successful telepsychiatry is the quality of the therapeutic relationship and the appropriateness of the treatment plan, both of which can be achieved through virtual consultations.
Experience the Ease of Telepsychiatry in New York with Wonder Years
Your first telepsychiatry appointment is an important step toward improving your mental health. At Wonder Years, we offer top-notch telepsychiatry services in New York, ensuring you receive the same high-quality care as in-person visits.
While initial appointments are conducted in person, subsequent sessions can be conveniently held online, providing flexibility and continuity. Our telepsychiatry visits are priced the same as regular appointments, making mental health care accessible and straightforward.
Contact us today to schedule your initial consultation and discover how our expert team can support your mental health journey through telepsychiatry.