How Childhood Trauma Affects Adulthood Relationships
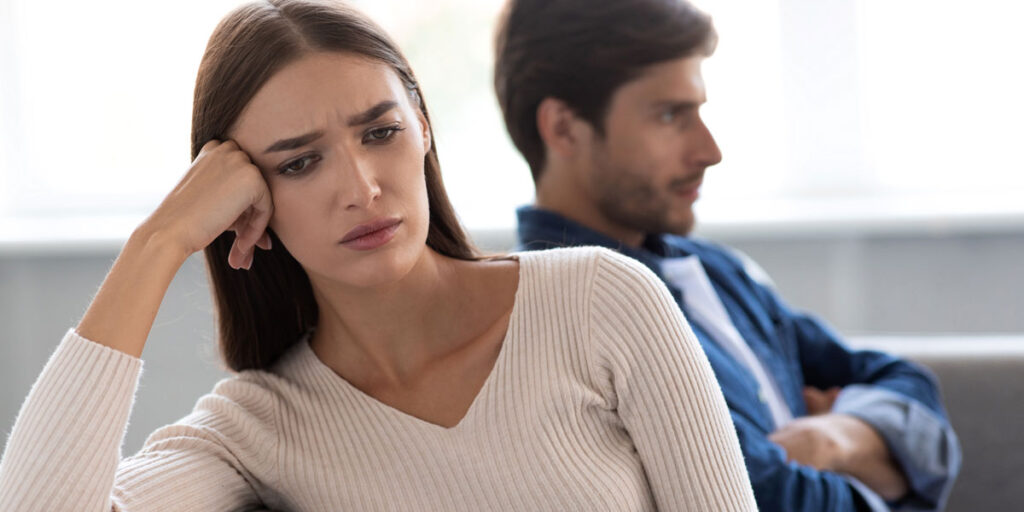
Childhood trauma can leave lasting scars that influence various aspects of an individual’s life, particularly their ability to form and maintain healthy relationships in adulthood. Understanding how childhood trauma affects adulthood relationships is essential for recognizing the challenges faced by survivors and finding ways to foster healing and growth. This blog post discusses the profound impact of early trauma on adult relationships, offering insights and strategies to support those on their journey to recovery.
The Lasting Impact of Childhood Trauma
- Emotional Dysregulation: One of the primary ways childhood trauma affects adulthood relationships is through emotional dysregulation. Individuals who experienced trauma in their formative years often struggle with managing their emotions, leading to intense and unpredictable reactions. This can create significant challenges in relationships, as partners may find it difficult to understand or cope with these emotional fluctuations.
- Trust Issues: Trust is a fundamental component of any healthy relationship. Childhood trauma, especially if it involves betrayal or abuse by a trusted caregiver, can severely impair an individual’s ability to trust others. Survivors may find it hard to believe that others have their best interests at heart, leading to a defensive or guarded approach to relationships. This mistrust can create barriers to intimacy and open communication.
- Attachment Styles: Attachment theory suggests that early interactions with caregivers shape our patterns of attachment in adult relationships. Childhood trauma can result in insecure attachment styles, such as anxious, avoidant, or disorganized attachment. These styles can manifest in adulthood as clinginess, fear of abandonment, difficulty in being vulnerable, or a tendency to push others away. Understanding one’s attachment style is a critical step in addressing relationship challenges rooted in early trauma.
The Role of Trauma Triggers
- Recognizing Triggers: Trauma triggers are sensory reminders of past traumatic events that can evoke strong emotional reactions. In the context of relationships, certain behaviors, words, or situations can trigger memories of childhood trauma, leading to disproportionate responses. Recognizing these triggers is vital for both partners, as it allows for more compassionate and informed interactions.
- Managing Reactions: Once triggers are identified, it’s important to develop strategies to manage reactions. Techniques such as mindfulness, grounding exercises, and therapy can help individuals regulate their emotions and respond more appropriately in the moment. Partners can also play a supportive role by providing a safe and understanding environment.
Building Healthy Relationships Post-Trauma
- Communication Skills: Effective communication is the foundation of any strong relationship. For trauma survivors, developing clear and assertive communication skills is essential. This involves expressing needs and boundaries without fear, as well as actively listening to one’s partner. Couples therapy can be a valuable resource in building these skills and fostering mutual understanding.
- Seeking Professional Help: Therapy is often necessary for individuals dealing with the effects of childhood trauma. A trained therapist can help survivors process their experiences, develop coping strategies, and work toward healing. Specific therapeutic approaches, such as Eye Movement Desensitization and Reprocessing (EMDR) or Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT), have proven effective in treating trauma-related issues.
- Creating Safe Spaces: Creating a sense of safety and stability within the relationship is crucial for trauma survivors. This involves consistent and reliable behavior from both partners, as well as a commitment to respect and empathy. Building trust takes time, but with patience and effort, it is possible to create a nurturing environment where both partners can thrive.
The Importance of Self-Care
- Personal Growth: Self-care and personal growth are essential for anyone recovering from childhood trauma. Engaging in activities that promote mental and physical well-being can help individuals feel more grounded and resilient. This might include regular exercise, mindfulness practices, pursuing hobbies, or spending time in nature.
- Support Systems: Having a strong support system outside of the romantic relationship is also important. Friends, family, and support groups can provide additional layers of understanding and encouragement. These connections can help alleviate some of the emotional burden and provide diverse perspectives on healing.
Transform Your Relationships with Wonder Years
Understanding how childhood trauma affects adulthood relationships is a vital step toward fostering healthier connections.
At Wonder Years, we specialize in helping individuals overcome the lasting impacts of childhood trauma. Our expert therapists offer both individual and group therapy, utilizing the most current and proven approaches for treating anxiety, depression, phobias, trauma, and relationship issues.
We provide a safe and supportive environment where you can work through your past and build healthier, more fulfilling relationships. Schedule an appointment today and begin your journey toward healing and personal growth. Your path to a brighter future starts here.